The number of different treatment groups that we have in any factorial design can easily be determined by multiplying through the number notation. As an example of a factorial design involving two factors an engineer is designing a battery for use in a device that will be subjected to some extreme variations in tempera- ture.
This design is called a quarter fraction of the full 25 or a 25-2 design a two to the five minus two design.
. 2 x 3 6 and that is the number of cells. Suppose there are 5 factors of interest A B C D and E and there are only enough resources for 16 experimental runs. Full factorial is 2k Fractional Factorial is 2kp Degree of fraction is 2p 25-5 Half-Fraction 2k Factorials This is one half the usual number of runs Similar to blocking procedure Choose a generator which divides efiects into two Based on pluses and minuses of one factor Deflning Relation.
For instance in our example we have 2 x 2 4 groups. The Advantages and Challenges of Using Factorial Designs. Also notice that each number in the notation represents one factor one independent variable.
21 the first dimension is the variable that is assumed to affect the speed of processing of process. A 12 fraction can be generated from any interaction but using the highest-order interaction is the. Example of Factorial Design.
Factorial Study Design Example 1 of 21 September 2019 With Results ClinicalTrialsgov. A 23 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables on a single dependent variable. We refer to the three levels of the factors as low 0 intermediate 1 and high 2.
21 displays a two-factorial design in which each factor is represented by a single dimension. This is an example of a 22 factorial design because there are two independent variables each with two levels. Study 7 factors with only 8 experiments.
Louis CSE567M 2008 Raj Jain Example. Neffect24 divided by df1 and turned into an F-ratio. This design is called a 2 1 fractional factorial design.
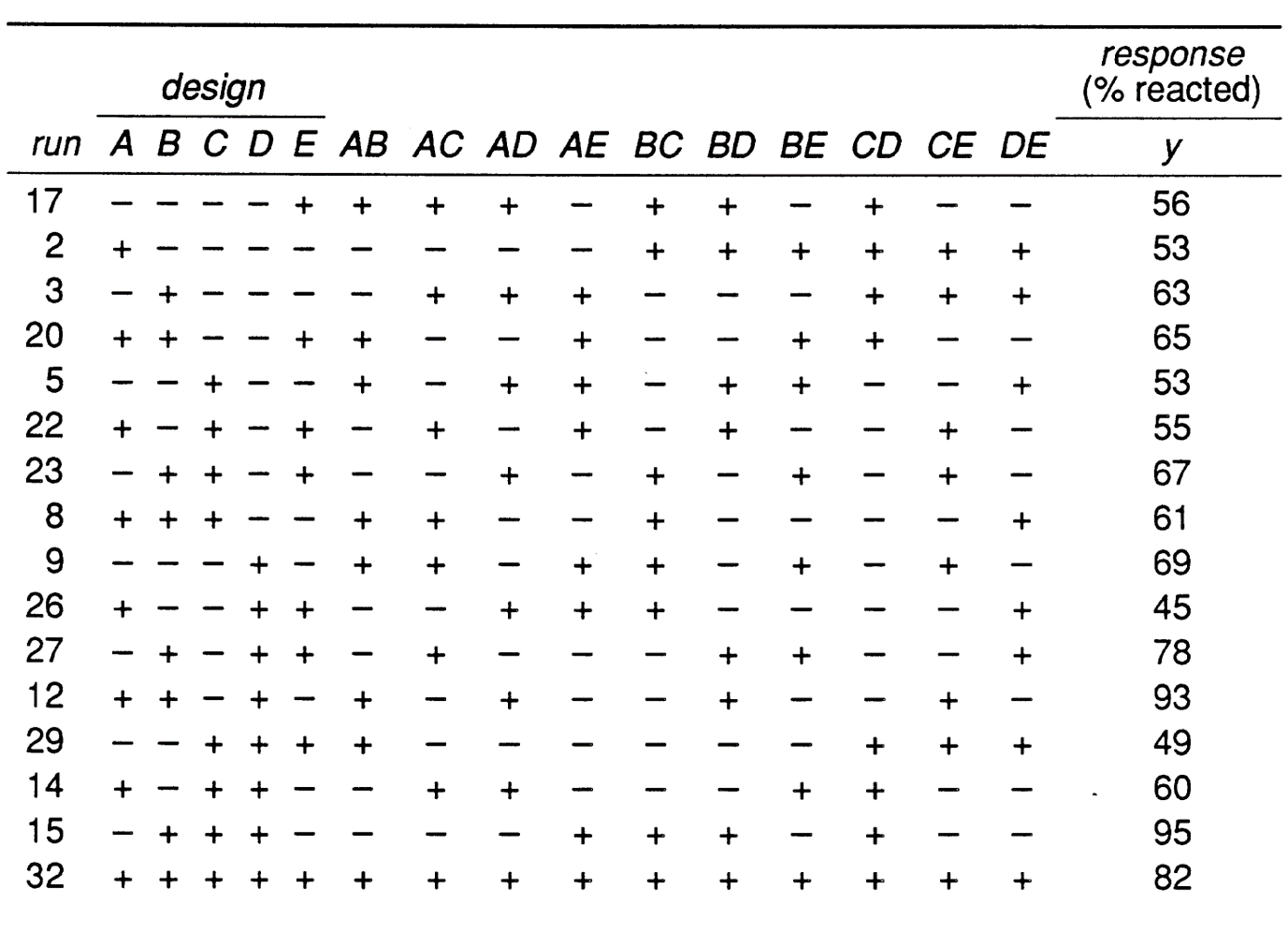
One of the big advantages of factorial designs is that they allow researchers to look for interactions between independent variables. In a typical situation our total number of runs is N 2 k p which is a fraction of the total number of treatments. A full factorial for the five factors A B C D E would have needed 25 32 runs.
Thus we want to run a 12 fraction of a 25 design. 19-4 Washington University in St. A Full Factorial Design Example.
The factors form a Cartesian coordinate system ie all combinations of each level of each dimension. In this type of design one independent variable has two levels and the other independent variable has three levels. So in this case either one of these.
For example in a 32 design the nine treatment combinations are denoted by 00 01 10 02 20 11 12 21 22. Weekly on the growth of a certain species of plant. 4 FACTORIAL DESIGNS 41 Two Factor Factorial Designs A two-factor factorial design is an experimental design in which data is collected for all possible combinations of the levels of the two factors of interest.
19-5 Washington University in St. A 2 2 factorial design has four conditions a 3 2 factorial design has six conditions a 4 5 factorial design would have 20 conditions and so on. The 3k Factorial Design is a factorial arrangement with k factors each at three levels.
The second number is a 3 so the second IV has 3 levels. The table below represents a 2 x 2 factorial design in which one independent variable is the type of psychotherapy used to treat a sample of depressed people behavioural vs cognitive and the other is the. This design is called a 25 1 fractional factorial design.
Partitioned into individual SS for effects each equal to. 3-2 The points for the factorial designs are labeled in a standard order starting with all low levels and ending with all high levels. 2k-p design allows analyzing k factors with only 2k-p experiments.
The average response from these runs can be contrasted with those from runs 1. 2k-2 design requires only one quarter of the experiments. The following information is fictional and is only intended for the purpose of illustrating key.
Full factorial example top wwwitlnistgov. Factorial Study Design Example With Results Disclaimer. An example of a full factorial design with 3 factors.
Use a fractional factorial design. In our notational example we would need 3 x 4 12 groups. For example runs 2 and 4 represent factor A at the high level.
Misuse of the ANOVA for 2k. We can also depict a factorial design in design notation. If equal sample sizes are taken for each of the possible factor combinations then the design is a balanced two-factor factorial design.
The following is an example of a full factorial design with 3 factors that also illustrates replication randomization and added center points. For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs. For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs.
A factorial experiment is carried out in the pilot plant to study the factors thought to influence the filtration rate of this product. So for example a 43 factorial design would involve two independent variables with four levels for one IV and three levels for the other IV. A factorial design is obtained by cross-combining of all the factors values.
Only 14 were run. Using our example above where k 3 p 1 therefore N 2 2 4. Is a service of the National Institutes of Health.
2k Factorial Models Design of Experiments - Montgomery Chapter 6 23 2k Factorial Design Each factor has two levels often labeled and Very useful design for preliminary analysis Can weed out unimportant factors Also allows initial study of interactions For general two-factor factorial model y ijk fi i fl j fifl ij ijk Have 1a 1 b. The first number is a 2 so the first IV has 2 levels. In general a 2k-p design is a frac12p fraction of a 2k design using 2k-p runs.
A fractional factorial design is useful when we cant afford even one full replicate of the full factorial design. For 2kdesigns the use of the ANOVA is confusing and makes little sense. High and watering frequency daily vs.
Two Level Factorial Experiments Reliawiki

2 K Factorial Design Tool Real Statistics Using Excel
Two Level Factorial Experiments Reliawiki

R How To Simulate An Unreplicated Factorial Design Cross Validated

Full Factorial Design For 2 Factors And 2 Levels A Design Matrix Download Scientific Diagram
Suppose The Experiment Was Ran With A Single Chegg Com

0 comments
Post a Comment